Call Option vs Put Option: Difference Explained with Examples
Stock Market Guides is not a financial advisor. Our content is strictly educational and should not be considered financial advice.
If you're having trouble understanding the difference between a call option and a put option, you're not alone. The terms themselves are not intuitive as far as we're concerned.
First of all, stock options are a tool in the stock market that allows investors to potentially benefit from the movement of stock prices.
They are leveraged, which means you can get more bang for your buck than you can compared to buying the corresponding stock. That extra bang can equate to either more profits or more losses.
When it comes to stock options, there are two types: call options and put options.
Here's a video that explains more about call vs put options:
Call Option vs Put Option Definition
Here is the difference between call options and put options in very simple terms:
Here is a simple way to look at it. If you think a stock price might go up, you could buy the stock to capture that potential increase. You could also buy a call option for the same purpose.
So in other words, buying a stock and buying a call option typically both involve the same hope: that the stock price will go up.
The opposite is true for put options. If you think a stock price might go down, you could short the stock to capture profit on that potential price decrease. You could also buy a put option for the same purpose.
So in other words, shorting a stock and buying a put option typically both involve the same hope: that the stock price will go down.
If you need more help getting up to speed on options, take a look at our guide to options trading for beginners.
Stock Market Guides

Stock Market Guides identifies option trading opportunities that have a historical track record of profitability in backtests.
Average Annualized Return
150.4%
Call Option Example
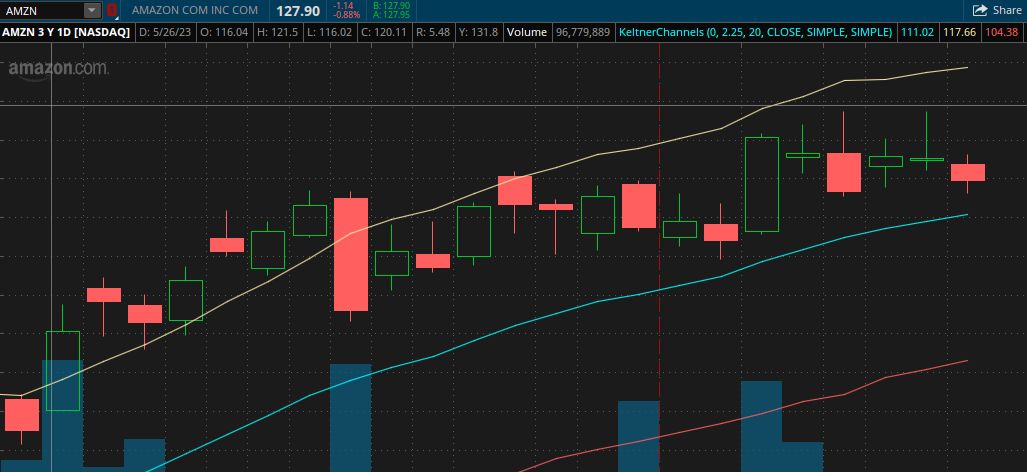
Here's an example of how a call option works. Imagine you're looking at Amazon stock.
That's a stock chart for Amazon. Maybe you see that the stock price has been consolidating and you think it's poised to boom within the next few weeks.
You could buy the stock itself, which is $127.90 per share as shown in the image above.
Or you could consider buying a call option.
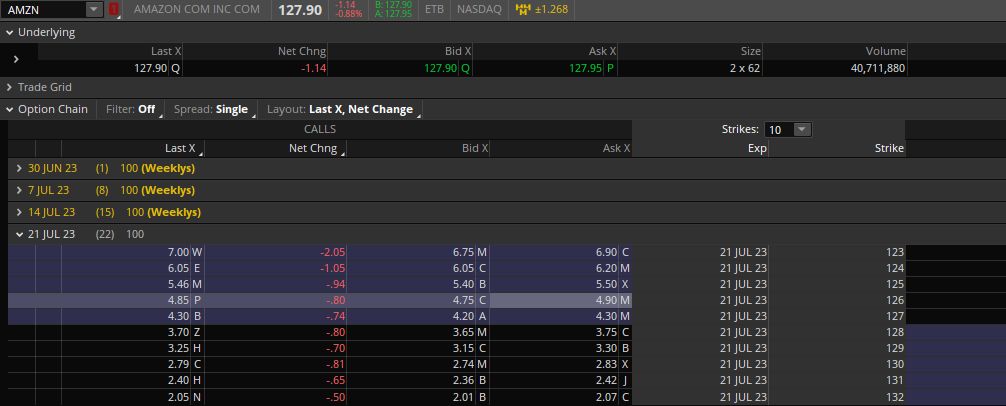
Here are call options that are available to buy for Amazon:
The options in the image have an expiration date that is about three weeks away. It shows the bid and ask of each call option that's available.
If we pick one example, say the 127 strike call options, you can buy them right now for 4.30.
Since option contracts each control 100 shares of stock, it means you would pay $430 to buy one call option contract (plus brokerage fees).
Compare that to buying 100 shares of the stock. That would require $12,790.
Now imagine that the stock price of Amazon went up to $140 in the next few weeks. Whether you own the stock or call option position in this example, the value will have gone up.
But the call option required a lot less capital due to the leverage that options afford investors.
Put Option Example
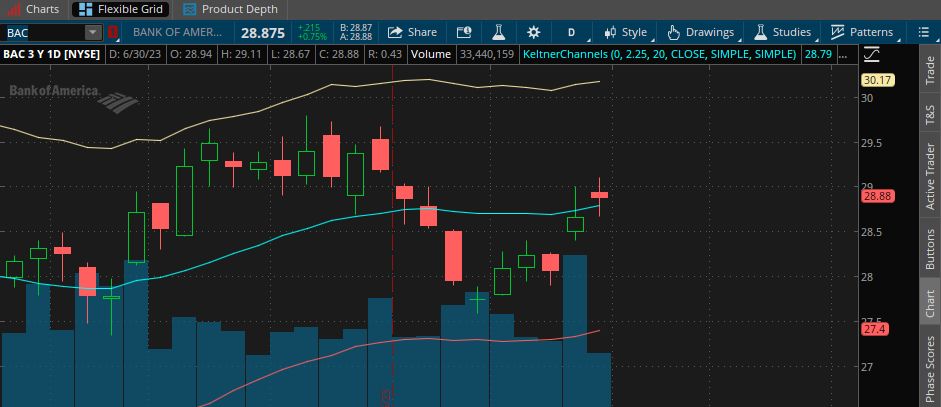
Here's an example of how a put option works. Imagine you're looking at Bank of America stock.
That's a stock chart for Bank of America shown in the Thinkorswim trading platform. Maybe you feel that the stock price is poised to sink within the next few weeks.
You could short the stock itself, which is trading at $28.88 per share as shown in the image above.
Or you could consider buying a put option.
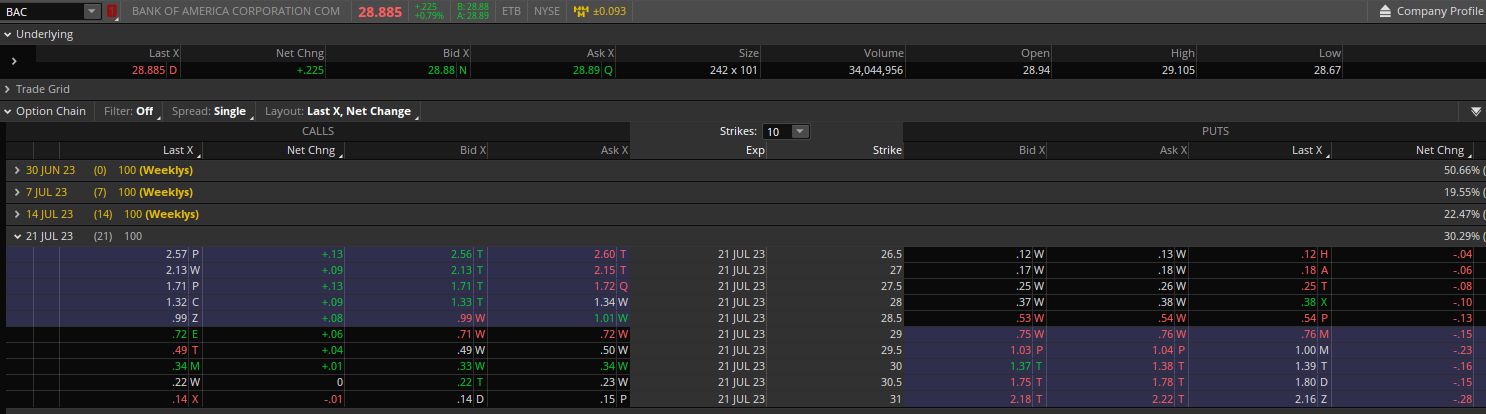
Here are put options that are available to buy for Bank of America:
You can see the put options at the far right of the option chain in the image.
The options in the image have an expiration date that is about three weeks away. It shows the bid and ask of each put option that's available.
If we pick one example, say the 29 strike put options, you can buy them right now for 0.76.
Since option contracts each control 100 shares of stock, it means you would pay $76 to buy one put option contract (plus brokerage fees).
Compare that to shorting 100 shares of the stock, which would require a lot more buying power.
Now imagine that the stock price of Bank of America went down to $27 in the next few weeks. Whether you short the stock or own the put option in this example, the value of your position will have gone up.
But the put option required a lot less capital due to the leverage that options afford investors.
Call vs Put Options: Other Considerations
The examples above offer a pretty simplistic idea of how call options and put options work. There are other factors at play to be aware of, though.
Overcoming Extrinsic Value in Calls and Puts
The price of many options includes some amount of extrinsic value. You can think of it as a premium you pay to be able to control the option.
Due to this extrinsic value, when you buy a call option, the price of the corresponding stock might have to go up some degree just to offset that premium before being able to turn a profit, particularly the longer you hold the option. And the same is true in reverse for a put option; the price of the underlying stock might have to go down to some degree just to offset that premium before being able to turn a profit.
Selling Calls vs Puts
Our examples above demonstrated how it works to buy call and put option. But it's also possible to sell them.
If you sell a call option, you benefit if the price of the underlying stock does not go up.
If you sell a put option, you benefit if the price of the underlying stock does not go down.
Selling options also has a different buying power impact than buying them.
Picking the Best Call and Put Options to Buy
If you like the idea of using options as an investment vehicle, then you can consider learning options trading strategies.
If you'd rather leave it to the pros but still want good option investment ideas, you can consider signing up for our options alert service.
Join Our Free Email List
Get emails from us about ways to potentially make money in the stock market.